Installation and getting started#
Installation#
You can install PyLumerical using pip.
First, create a virtual environment and activate it to avoid dependency conflicts and to keep your global Python environment clean.
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
python -m venv .venv
.venv\\Scripts\\activate.bat
python -m venv .venv
.venv\\Scripts\\Activate.ps1
Then, upgrade pip to the latest version, and install PyLumerical with the package name ansys-lumerical-core.
python -m pip install -U pip
python -m pip install ansys-lumerical-core
Tip
Using a virtual environment isn’t a requirement, but it’s a best practice for Python development.
Requirements#
You must have an Ansys Lumerical GUI license to use PyLumerical. For more information, please visit the licensing page on the Ansys Optics website.
In addition, you must also have Lumerical 2022 R1 or later installed on your computer. Upon importing PyLumerical, the autodiscovery function automatically locates the Lumerical installation path. If it fails to do so, you must set the path manually using ansys.lumerical.core.autodiscovery.locate_lumerical_install().
My first PyLumerical project#
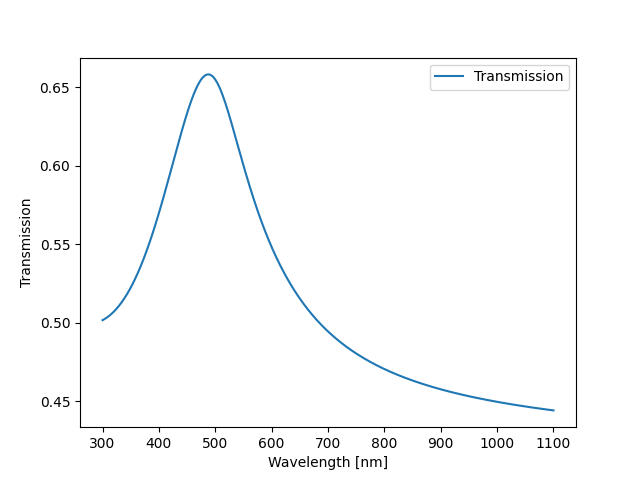
The code snippet below provides simple project of using PyLumerical and Python library matplotlib to visualize the transmission of a gold thin film illuminated by a plane wave. Matplotlib isn’t automatically installed with PyLumerical, so you need to install it separately in your environment.
import ansys.lumerical.core as lumapi
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Ensure matplotlib is installed in your environment first
with lumapi.FDTD() as fdtd:
lambda_range = np.linspace(300e-9, 1100e-9, 500)
c=2.99792458e8
f_range = c/lambda_range
au_index = fdtd.getfdtdindex("Au (Gold) - CRC", f_range, np.min(f_range), np.max(f_range)) # Use the getfdtdindex command to obtain the correct complex index for gold
stackRT_result = fdtd.stackrt(np.transpose(au_index), np.array([10e-9]), f_range) # Use the stackrt command to calculate the transmission and reflection
# Visualize using matplotlib
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(lambda_range*1e9, stackRT_result["Ts"], label="Transmission")
ax.set_xlabel("Wavelength [nm]")
ax.set_ylabel("Transmission")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
This simulation returns the following result.
Further resources#
Information on key concepts of PyLumerical.
Reference for the PyLumerical API.
Gallery of examples using PyLumerical.
Recommended examples#
Recommended examples to further build your understanding of PyLumerical and its capabilities.

